Organizations must continuously adapt to stay competitive in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape. One such evolution is the adoption of multi-cloud GPU clusters and managed services, a topic recently discussed in a webinar by ACCRETS International.
This blog post explores the key points from that webinar, offering insights into the current and future trends in cloud adoption, the advantages of various cloud strategies, and the steps organizations should take to modernize their applications and infrastructure.
Current and Future Trends in Cloud Adoption
Public Cloud Adoption
Despite the availability of public cloud services for over a decade, many larger corporations, particularly in Singapore, have been slow to embrace this technology. Concerns about security, skepticism, and cost issues often impede adoption.
While public cloud services are ideal for public-facing applications, they are not always suitable for internal systems like SAP, which can become costly and inefficient when migrated to the public cloud.
Persistence of Traditional Architectures
A significant number of organizations still rely on traditional three-tier architecture for their backroom operations, representing about 80% of IT spending. This persistence is partly due to a lack of talent at various organizational levels. Many executives and developers are not up-to-date with modern technologies such as cloud containers, and financial constraints prevent a comprehensive shift to new systems.
The Rise of Digital Banks
In contrast, the financial sector, especially digital banks, has been quick to adopt new technologies to reduce costs and enhance services. These institutions leverage AI to analyze borrowing patterns and predict potential loan defaults, showcasing a strategic use of AI for risk management.
The Case for Multi-Cloud GPU Clusters and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Challenges with Public Cloud
Public cloud services come with unpredictable costs and limitations in operating system usage, making large-scale migration challenging. Migrating traditional applications to the public cloud involves extensive steps, including OS installation, application setup, data migration, backup, and monitoring setup, which are often impractical.
Advantages of Private Cloud
Private clouds offer more secure, cost-effective, and predictable solutions. Creed International, for example, has successfully migrated small companies from on-premises to their private cloud over a weekend, highlighting the efficiency and advantages of private cloud solutions.
The Path Forward: Embracing New Technologies
Modernizing Applications
Modernizing applications requires a strategic approach, focusing on critical ones with a long-term strategy. A comprehensive overhaul in a single year is impractical; a phased approach over ten years is more feasible.
The Impact of Large Language Models (LLM)
Technologies like ChatGPT have significantly accelerated development times. Creed International’s document management system, initially developed over two years using traditional AI methods, was redeveloped in three languages within six months using LLM. This demonstrates the immense potential and speed of development with LLM.
The Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Landscape
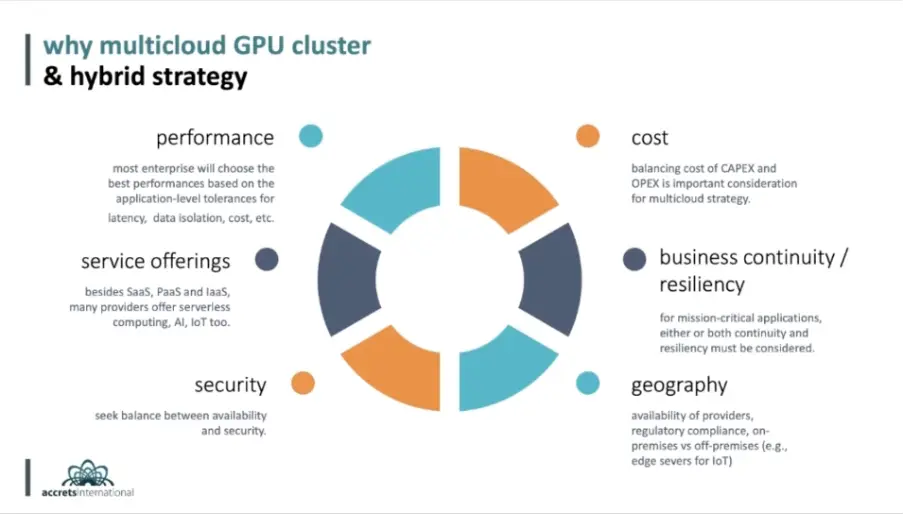
Service Offerings
Public cloud offers various services, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), with advanced AI and IoT capabilities. However, for in-house applications, a private cloud may be more suitable. Creed International recently helped a large government corporation set up an on-premises PaaS system using modern technologies like Docker and Kubernetes.
Statistics and Trends
Nearly 89% of organizations have a multi-cloud strategy, with 80% adopting a hybrid cloud infrastructure. On average, organizations use 2.6 public and 2.7 private clouds, indicating a balanced approach. However, a significant portion of applications remains on traditional systems, which companies need to rationalize and modernize.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Options
Public Cloud
- Pros: Highly scalable, massive resource pools, cost-effective for public-facing applications, reliable disaster recovery options.
- Cons: Expensive bandwidth costs, less secure, no customization options.
Private Cloud
- Pros: Exclusive control, enhanced security, flexible connectivity options, easier migration.
- Cons: Higher hardware investment, need for skilled professionals, fewer built-in services compared to public clouds.
Strategy for Cloud Adoption
To determine the best cloud strategy, organizations should:
- Inventory Applications and Infrastructure: Identify the importance and priority of each component.
- Research Technology Landscape: Understand available technologies and choose the most effective solutions, like LLM for AI projects.
- Build a Roadmap: Develop a phased plan for modernization with a clear budget.
Conclusion
Organizations need to embrace new technologies and develop strategic plans for cloud adoption to stay competitive. Multi-cloud GPU clusters and managed services offer a path forward, combining the best aspects of public and private clouds. Creed International is committed to assisting organizations with their cloud strategies, ensuring a seamless transition to modern infrastructure.
For more information or assistance, feel free to reach out. The future is in the cloud—it’s time to embrace it!
Holding a degree in B.Tech in Information Technology with an experience of 5 years in the industry. I am a cloud computing and IT Infrastructure enthusiast, who loves to share knowledge with the world.